이번 포스팅에서는 sensor 값을 받은 데이터를 i2c를 통해 젯슨나노에 값을 보내고 젯슨에서는 그 값을 서버에 post하는 작업에 대해 포스팅해보겠다.
이전 작업이 어려운거고 이번 포스팅은 기록이라고 보면 되겠다.
이번 포스팅에서 영상은 제외했다. 참고바란다.
시작하겠다.
개발 환경
- Jetson Nano B01 4GB
- Arduino Due
- Ubuntu 20.04
먼저 Fan 3개를 PWM제어를 할 예정이고, tach핀을 사용하여 rpm을 측정하고 그 rpm 값을 서버에 보내는 걸 해보겠다.
* 전압은 fan, 아두이노 듀에 둘다 외부 전압으로 준다는 점 유의바란다.
순서는 다음과 같다.
1. 아두이노 듀에에서 PWM제어를 하고, tach핀을 활용하여 RPM 측정해보기
2. RPM이 맞다는 가정하에 ( 레퍼런스 장비로 타코미터 장비로 측정 및 오실로스코프로 확인 ) RPM i2c로 값 전송
3. 젯슨에서 받은 값 서버에 전송
이렇게 세 단계로 이루어져 있다.
아두이노 듀에에서 PWM제어를 하고, tach핀을 활용하여 RPM 측정해보기
이 부분은 어려운게 아니다. 우리는 아두이노 IDE를 활용할 것이다.
첫 번째로 듀에에서 PWM 제어를 한다.
M1_P1_1000이 들어오면 듀티사이클 약 78% 정도 된다.
M1_P1_2000이 들어오면 듀티사이클은 0%이다. (fan 정지상태)
M1_P1_이외의 값, 이 들어오면 듀티사이클은 36%로 둔다.
듀티사이클이란?
신호의 한 주기(period)에서 신호가 켜져있는 시간의 비율을 백분율로 나타낸 수치
pwm이 256이니 200 / 256 * 100 = 78.125%
#define fanCount 3
const uint8_t pwmPins[fanCount] = {8,9,10};
const uint8_t minPwm = 30;
uint8_t currentPWMs[fanCount] = {30,30,30};
bool startReceived = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
for(int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++){
pinMode(pwmPins[i], OUTPUT);
analogWrite(pwmPins[i], minPwm);
}
delay(100);
}
void loop() {
if(Serial.available() > 0){
String input = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
input.trim();
if(input.startsWith("M1_P")){
int fanIndex = input.substring(4,5).toInt() - 1;
int fanSpeed = input.substring(6).toInt();
if(fanSpeed == 1000){
currentPWMs[0] = 200;
currentPWMs[1] = 200;
currentPWMs[2] = 200;
}else if(fanSpeed == 2000){
currentPWMs[0] = 0;
currentPWMs[1] = 0;
currentPWMs[2] = 0;
}else{
currentPWMs[0] = 100;
currentPWMs[1] = 100;
currentPWMs[2] = 100;
}
}else if(input == "start"){
startReceived = true;
}
}
if(startReceived == true){
for(int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++){
Serial.print(currentPWMs[i]);
if(i < fanCount - 1){
Serial.print(",");
}
}
Serial.println();
startReceived = false;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
analogWrite(pwmPins[j], currentPWMs[j]);
}
}
이번엔 RPM을 측정해 보겠다.
const int pwmPins[] = {8, 9, 10}; // 팬의 PWM 핀들
const int tachPins[] = {2, 3, 4}; // 팬의 TACH 핀들
const int fanCount = 3; // 팬의 수
volatile int tachCounters[fanCount] = {0, 0, 0};
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
const long interval = 1000; // 1초마다 RPM 계산
int targetRPMs[fanCount] = {900, 900, 900}; // 목표 RPM
int currentPWMs[fanCount] = {0, 0, 0}; // 현재 PWM 값
bool targetReached[fanCount] = {true, true, true}; // 목표 RPM 도달 여부 추적
const int minPWM = 0; // 최소 PWM 값
bool startReceived = false;
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++) {
pinMode(tachPins[i], INPUT_PULLUP); // TACH 핀을 입력으로 설정
pinMode(pwmPins[i], OUTPUT); // PWM 핀을 출력으로 설정
analogWrite(pwmPins[i], 30); // 초기 PWM 값을 0으로 설정
}
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[0]), tachCounterISR0, FALLING);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[1]), tachCounterISR1, FALLING);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[2]), tachCounterISR2, FALLING);
Serial.begin(9600);
delay(100);
//Serial.println("Enter target RPMs for each fan in the format '2000 3000 1500' or 'M1_P1_2000':");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String input = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
input.trim();
// 새로운 입력 형식 M1_P 처리
if (input.startsWith("M1_P")) {
int fanIndex = input.substring(4, 5).toInt() - 1; // 팬 인덱스 (0부터 시작)
int fanSpeed = input.substring(6).toInt(); // 입력된 RPM 값
if (fanIndex >= 0 && fanIndex < fanCount) {
targetRPMs[fanIndex] = fanSpeed;
targetReached[fanIndex] = false; // 새로운 목표 RPM이 설정되면 도달 플래그 초기화
}
} else if(input == "start") {
startReceived = true;
}
}
if (startReceived == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++) {
if(i < fanCount - 1){
Serial.print(",");
}
Serial.print(targetRPMs[i]);
}
startReceived = false;
}
// 1초 간격으로 RPM 계산 및 PWM 조정
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis;
for (int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++) {
int realRPM = (tachCounters[i] * 60) / 2;
tachCounters[i] = 0; // tachCounter 초기화
int error = targetRPMs[i] - realRPM;
int pwmStep = 0;
if (abs(error) > 1000) {
pwmStep = 50;
} else if (abs(error) > 450) {
pwmStep = 10;
} else if (abs(error) > 200) {
pwmStep = 5;
} else if (abs(error) > 30) {
pwmStep = 1;
}
if (pwmStep > 0) {
currentPWMs[i] += (error > 0) ? pwmStep : -pwmStep;
currentPWMs[i] = constrain(currentPWMs[i], minPWM, 255);
analogWrite(pwmPins[i], currentPWMs[i]);
}
if (abs(error) <= 30 && !targetReached[i]) {
Serial.print("M1_P");
Serial.print(i+1);
Serial.print("_");
Serial.print(targetRPMs[i]);
Serial.println();
targetReached[i] = true;
}
Serial.print("Fan ");
Serial.print(i + 1);
Serial.print(" | Target RPM: ");
Serial.print(targetRPMs[i]);
Serial.print(" | Real RPM: ");
Serial.print(realRPM);
Serial.print(" | PWM: ");
Serial.println(currentPWMs[i]);
}
}
}
void tachCounterISR0() {
tachCounters[0]++;
}
void tachCounterISR1() {
tachCounters[1]++;
}
void tachCounterISR2() {
tachCounters[2]++;
}
이렇게 잘 측정되는 것을 알 수 있다.
주의사항
Fan 3개를 구동시키는 거기때문에 높은 전압에서 스텝다운을 사용해 안정적인 전력 공급을 하는게 좋다.
그리고 꼭 전압 전류를 잘 따져서 설치해줘라
특히 선 굵기마다 전류를 전달할 수 있는 크기가 정해져 있다. ( 본인은 AWG22를 사용중)
다음은 RPM측정인데, 타코미터로 측정 결과 오차 범위 30 이내 인것을 확인했으므로 넘어간다.
RPM 값 i2c로 값 전송
아두이노 코드
#include <PMS.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDRESS 0x57
// Register addresses
#define WRITE_REGISTER 0x01
#define READ_REGISTER 0x02
#define START_SIGNAL 0xA0
String con_data = "0,0,0";
const uint8_t pwmPins[] = {8, 9, 10};
const uint8_t tachPins[] = {2, 3, 4};
const uint8_t fanCount = 3;
volatile int tachCounters[fanCount] = {0, 0, 0};
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
const long interval = 1000;
int targetRPMs[fanCount] = {900, 900, 900};
int currentPWMs[fanCount] = {30, 30, 30};
bool targetReached[fanCount] = {true, true, true};
const int minPWM = 30;
PMS pms1(Serial1);
PMS::DATA data1;
PMS pms2(Serial2);
PMS::DATA data2;
PMS pms3(Serial3);
PMS::DATA data3;
bool startReceived = false;
//uint16_t d1, d2, d3;
void setup() {
Wire.begin(SLAVE_ADDRESS);
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // 읽기 요청에 대한 핸들러
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // 쓰기 요청에 대한 핸들러
delay(100);
for (int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++) {
pinMode(tachPins[i], INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(pwmPins[i], OUTPUT);
analogWrite(pwmPins[i], minPWM);
}
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[0]), tachCounterISR0, FALLING);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[1]), tachCounterISR1, FALLING);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(tachPins[2]), tachCounterISR2, FALLING);
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial1.begin(9600);
Serial2.begin(9600);
Serial3.begin(9600);
delay(100);
pms1.passiveMode();
pms2.passiveMode();
pms3.passiveMode();
//Serial.println("Enter target RPMs for each fan in the format '2000 3000 1500' or 'M1_P1_2000':");
}
void loop() {
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis;
for (int i = 0; i < fanCount; i++) {
int realRPM = (tachCounters[i] * 60) / 2;
tachCounters[i] = 0;
int error = targetRPMs[i] - realRPM;
int pwmStep = 0;
if (abs(error) > 1000) {
pwmStep = 20;
} else if (abs(error) > 450) {
pwmStep = 10;
} else if (abs(error) > 200) {
pwmStep = 5;
} else if (abs(error) > 30) {
pwmStep = 1;
}
if (pwmStep > 0) {
currentPWMs[i] += (error > 0) ? pwmStep : -pwmStep;
currentPWMs[i] = constrain(currentPWMs[i], minPWM, 255);
analogWrite(pwmPins[i], currentPWMs[i]);
}
if (abs(error) <= 30 && !targetReached[i]) {
Serial.print("M1_P");
Serial.print(i+1);
Serial.print("_");
Serial.print(realRPM);
Serial.println();
targetReached[i] = true;
}
Serial.print("Fan ");
Serial.print(i + 1);
Serial.print(" | Target RPM: ");
Serial.print(targetRPMs[i]);
Serial.print(" | Real RPM: ");
Serial.print(realRPM);
Serial.print(" | PWM: ");
Serial.println(currentPWMs[i]);
}
}
}
void receiveEvent(int howMany) {
int registerAddress = Wire.read();
if (registerAddress == WRITE_REGISTER) {
char buffer[32];
int index = 0;
while (Wire.available() > 0 && index < sizeof(buffer) - 1) {
buffer[index++] = Wire.read();
}
buffer[index] = '\0';
String receivedString = String(buffer);
Serial.print("received: ");
Serial.println(receivedString);
int fanIndex = receivedString.substring(4, 5).toInt() - 1;
int fanSpeed = receivedString.substring(6).toInt();
if (fanIndex >= 0 && fanIndex < fanCount) {
targetRPMs[fanIndex] = fanSpeed;
targetReached[fanIndex] = false;
}
}
else if (registerAddress == READ_REGISTER && Wire.available() > 0) {
int signal = Wire.read();
if (signal == START_SIGNAL) {
startReceived = true;
}
}
}
void requestEvent() {
if (startReceived) {
startReceived = false;
con_data = (String)targetRPMs[0] + "," + (String)targetRPMs[1] + "," + (String)targetRPMs[2];
int len = con_data.length() + 1;
char buffer[len];
con_data.toCharArray(buffer, len);
Wire.write((uint8_t*)buffer, len);
Serial.println(buffer);
}
}
// ISR
void tachCounterISR0() {
tachCounters[0]++;
}
void tachCounterISR1() {
tachCounters[1]++;
}
void tachCounterISR2() {
tachCounters[2]++;
}
젯슨나노 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "i2c.h"
#include <thread>
#include "http.h"
#define SLAVE_ADDRESS_1 0x57 // 첫 번째 아두이노의 I2C 주소
#define SLAVE_ADDRESS_2 0x60 // 두 번째 아두이노의 I2C 주소
// 프로그램 종료 시 클린업
void cleanup(int signum) {
std::cout << "\n프로그램을 종료합니다." << std::endl;
exit(0);
}
// 명령어 파싱 함수
bool parseCommand(const std::string &command, int &arduinoNum, std::string &action) {
if (command.size() < 4 || command[0] != 'M' || command[2] != '_') return false;
arduinoNum = command[1] - '0';
action = command.substr(3, 2); //P1 or P2 or P3
return true;
}
int main() {
signal(SIGINT, cleanup);
std::string command;
int address, arduinoNum;
std::string action;
std::string url = "http://114.71.220.59:2021/Mobius/justin/ss/motor";
std::cout << "start" << std::endl;
while (true) {
std::cout << "명령을 입력하세요: ";
std::cin >> command;
if (!parseCommand(command, arduinoNum, action)) {
std::cerr << "잘못된 명령 형식입니다. 형식: M?_ACTION" << std::endl;
continue;
}
// 아두이노 번호에 따라 주소 설정
if (arduinoNum == 1) {
address = SLAVE_ADDRESS_1;
} else if (arduinoNum == 2) {
address = SLAVE_ADDRESS_2;
} else {
std::cerr << "잘못된 아두이노 번호입니다. 1 또는 2를 입력하십시오." << std::endl;
continue;
}
int file = openI2CDevice(address);
if (file < 0) continue;
if (action == "P1" || action == "P2" || action == "P3") {
sendCommand(file, command);
} else if (action == "READ") {
std::string recevieData = readData(file);
std::cout << recevieData << std::endl;
send_value_to_server(url, recevieData);
} else {
std::cerr << "알 수 없는 명령입니다: " << action << std::endl;
}
close(file);
}
cleanup(0);
return 0;
}
실제 실행 결과
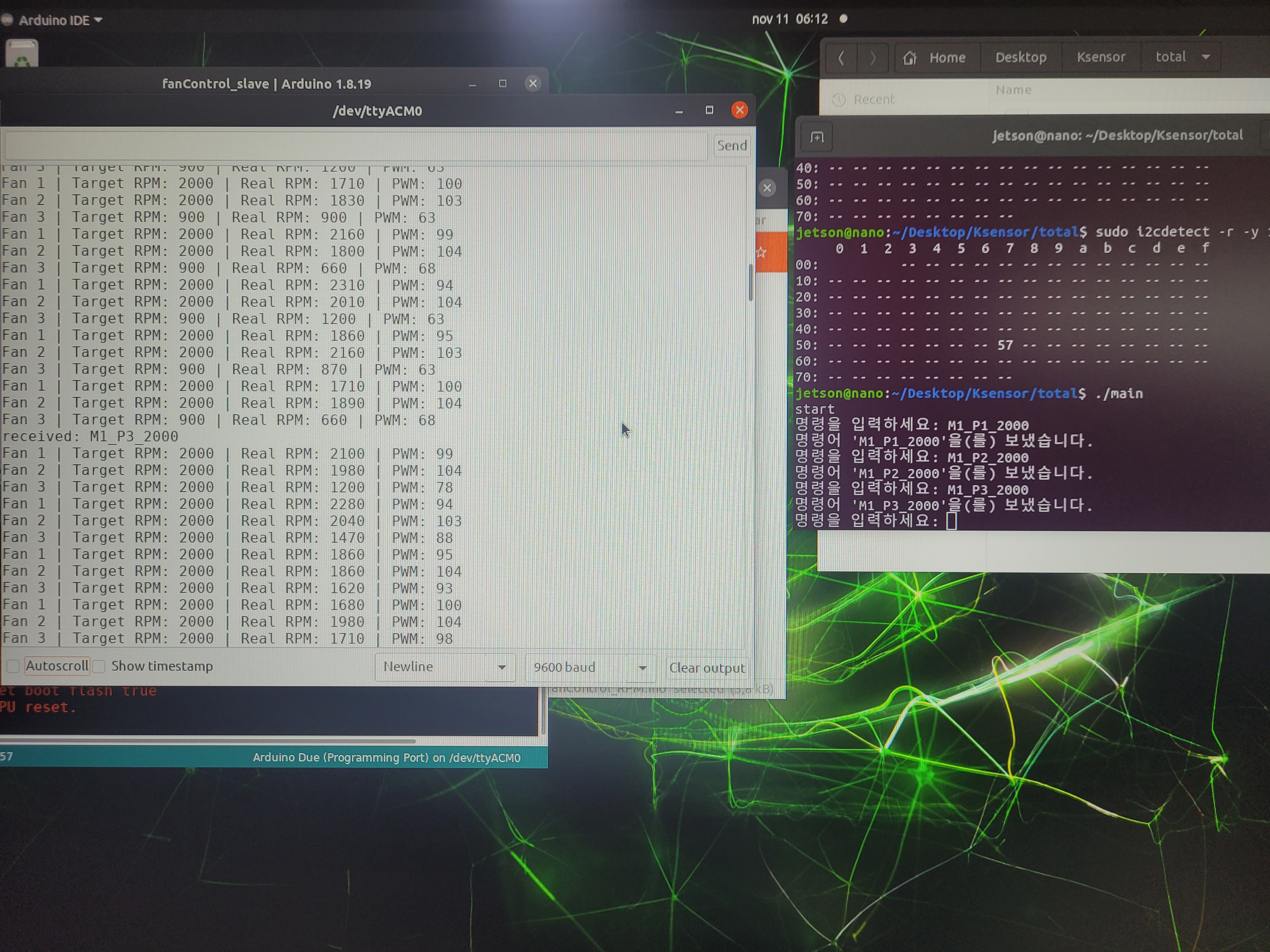
젯슨에서 받은 값 서버에 전송
위 코드에서 READ 명령어로 전송하면 서버에 전송되니 참고 바란다.
'Jetson > i2cProject_with_Jetson' 카테고리의 다른 글
| server에 올라오는 명령어에 따라 Fan 제어 2) (0) | 2024.11.15 |
|---|---|
| server에 올라오는 명령어에 따라 Fan 제어 1) (1) | 2024.11.14 |
| i2c로 받은 데이터 server에 post - Jetson Nano requests a value from Arduino via i2c, then uploads it to a server (2) | 2024.11.11 |
| i2c로 받은 데이터 server에 post - send data with Jetson nano (0) | 2024.11.11 |
| 제품 변경 (아두이노 Due) (2) | 2024.11.07 |